The first week of the 1975 Regional America program focused on the people of the Northern Plains (North Dakota, South Dakota, Nebraska and Kansas), particularly on the occupational life-styles related to agriculture and livestock. This is the region that is called the "breadbasket" and the economy of the area is based on grain crops, feed crops, and livestock production. The Smithsonian represented the agriculture of the area by growing on the Festival site wheat (the principal grain crop), alfalfa (a principal feed crop), and some typical plains grasses as well as sorghum and sunflowers. Livestock grazed on the National Mall and were used in demonstrations of herding techniques. Visitors saw varieties of threshing from individual manual techniques to modern mechanical combines. A daily tractor pull contest demonstrated not only the skills of the farmers in operating equipment, but also the pride they take in the power of their own carefully maintained machinery.
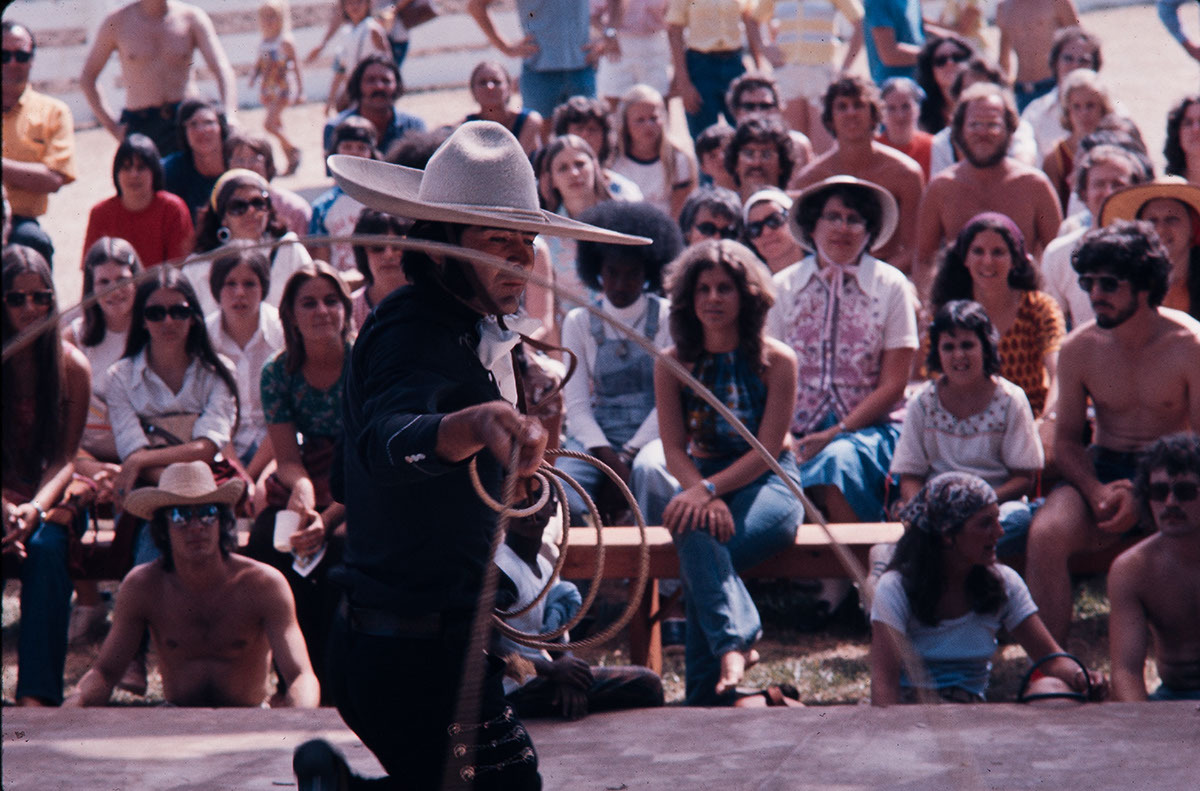
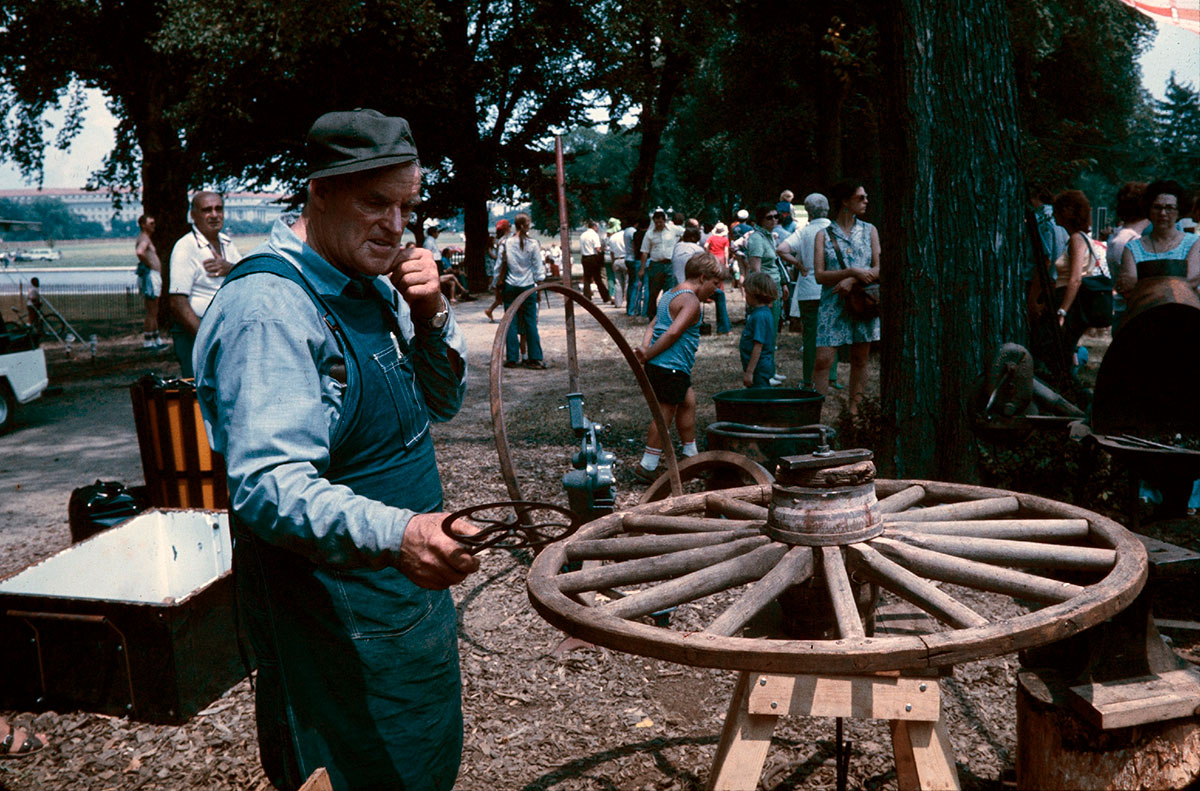
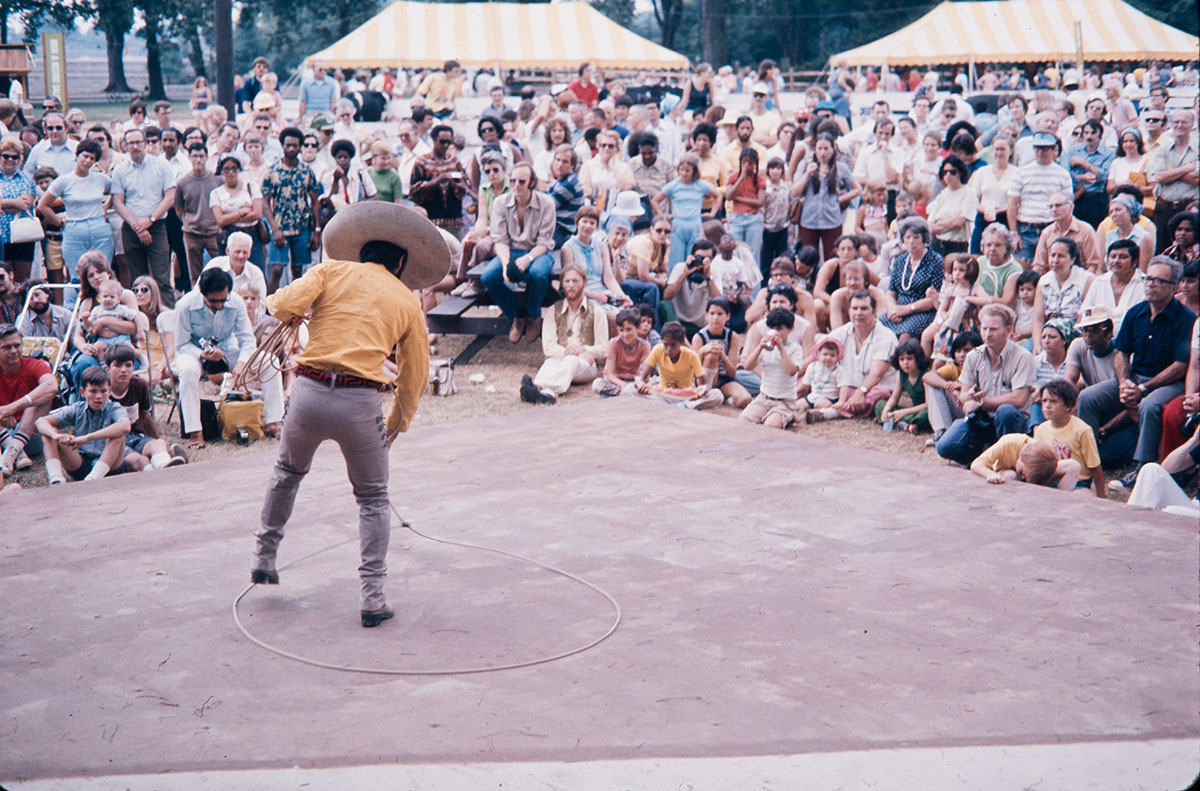
Craft presentations included associated occupational and domestic crafts. For example, livestock-related crafts such as those involved with maintenance, auctioneering, leatherworking, blacksmithing, wagon making and repair, and metal working were highlighted, as well as key occupational skills related to livestock include horse handling, sheep shearing, and ropework. Functional but decorative domestic crafts were also demonstrated: piece quilts, braided and rag rugs, corn husk and rag dolls, toys carved from chips, noisemakers, whimmy diddles.
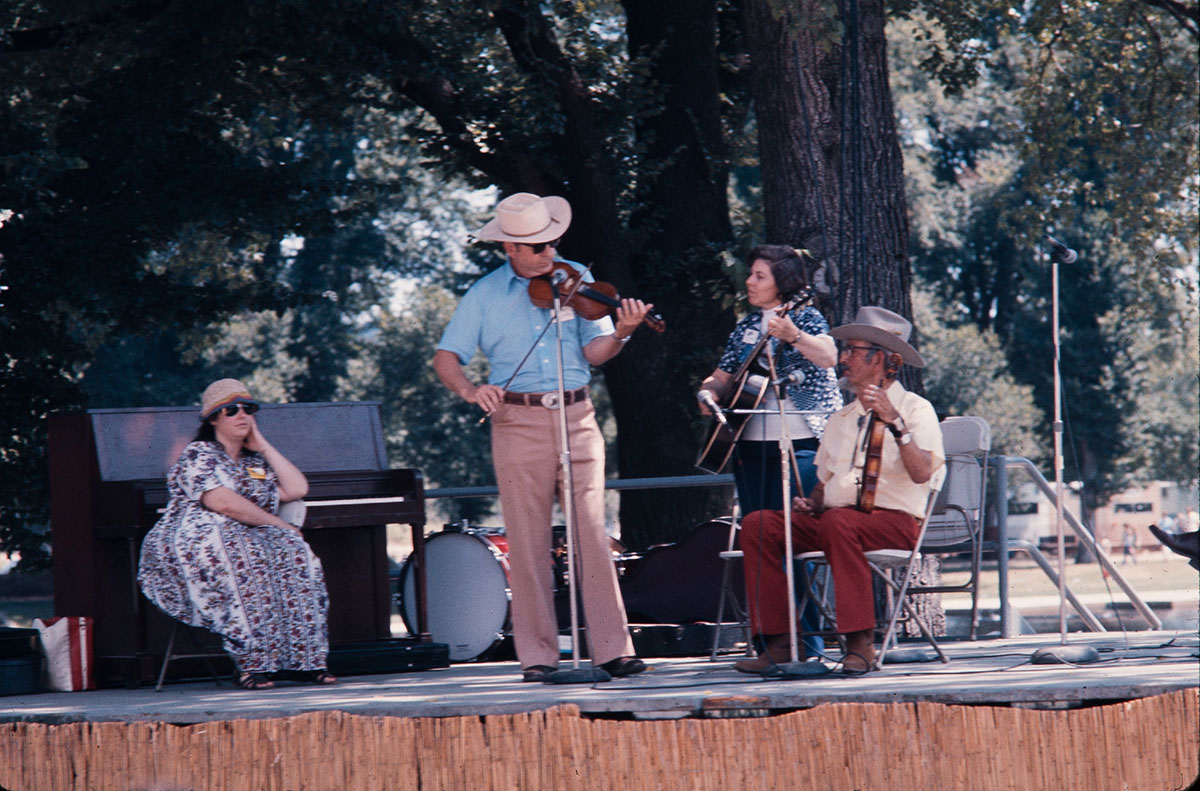
Festival visitors could see and participate in a variety of folk dancing by different ethnic groups who settled in the Plains: Germans, Scandinavians, Ukrainians and Czechs. Northern Plains music is characteristically performed on instruments practiced in isolation such as the fiddle.These are usually played solo, but at the Festival they were also performed in combination.
The character of the California Heartland region (second week of the Festival) is expressed by its flamboyant image, diverse landscape, and - of utmost importance - a 'Mediterranean' climate that makes outdoor living possible. It is also an area rich in ethnic communities, and many of these were featured at the 1975 Festival.
Mexican American muralists from East Los Angeles completed a mural depicting their contribution to the Festival. Paper flower making and piñata making were demonstrated and taught to visitors, as were masa grinding and tortilla and tamale making. Chinese Americans from the San Francisco area performed a shadow puppet play twice daily. Various crafts including kite-making and the construction of paper ribbon fish welcomed audience participation. Three traditional games (an early form of yoyo, shuttlecock and cat's cradle) were demonstrated and taught.
Portuguese American fisherfolk demonstrated boat building as well as net and lure making accompanied by traditional sea chanteys. A highlight of the Portuguese community is the "Festa da Espiritu Santu", a celebration involving a parade of decorated cows, ceremonial milking, a milk and bread feast and a traditional contest between solo singers who improvise verses, enacted on the Festival site from July 2 to 4.
Unique to San Francisco is the tradition of cable car bell ringing. Cable car gripmen announced each session at the main California stage and dance floor, and competed for the bell ringing championship. A Greek father and son demonstrated traditional woven straw beehive construction and discussed beekeeping and the agricultural use of bees. California Armenians wove rugs and spun wool. The joys of sociable dancing were shared by square dances, Portuguese chamaritas, Phillippine tinakling and an evening of waltzes. There were also examples of solo singing by Portuguese, Anglo, French, and black singers and group singing by Molokans, Anglos, Chicanos and blacks.
Administrator for the Regional America program was William K. McNeil, with Charles Camp as Research Coordinator; Rayna Green served as Consultant.